Did you know that 81% of small publishers monetize their ad inventories using Google Ad Manager? Whether you knew it or not, the statistic must have astounded you. The market share of Google Ad Manager proves how it is leading in the advertising industry.
However, several of Google’s publishing products make it difficult for beginners to understand the difference. And how each product works. If you are also in the same boat, this article is catered to you. Here, we will discuss everything related to Google Ad Manager (Google Ad Manager tutorial), from the basics to how to set it up and start serving ads. So, shall we start?
Before knowing Google Ad Manager, first know
Table of Contents
- What Ad Manager Is?
- Google Ad Manager
- Google Ad Manager Versions
- Basic Google Ad Manager Terminologies
- How Does Google Ad Manager Work?
- Google Ad Manager: When Do You Need It?
- Is Google Ad Manager an Ad Server or an SSP?
- Google Ad Manager vs. Google AdSense
- Google Ad Manager vs. Google Ads
- Google Ad Manager Account: How to Set It Up?
- How do you Link Google AdSense to Google Ad Manager?
- Ad formats Offered in Google Ad Manager
- Google Ad Manager Price
- Google Ad Manager Benefits
- Organizing your Ad Partners in Google Ad Manager
- Final Thoughts
What Ad Manager Is?
Ad Manager is a platform that helps publishers with ad management, i.e, optimizing their website with ads. They help publishers manage, test, and track the performance of the website ads across different devices and channels.
Ok, now, what is
Google Ad Manager
It is a Google product used by publishers for ad management. It is an ad server. But what’s an ad server? It is a platform that helps publishers with efficient ad serving. Publishers use GAM to define, manage, and monitor ad inventories on their web, mobile app, or video ad inventories to display various types of ads.
Being an ad server, Google Ad Manager is the central place that manages all direct and indirect advertisers, ad networks, ad exchanges, and other ad-tech partners. It enables the publishers to:
- Display ads on the website, including direct-sold ads, programmatic ads, and house (publisher’s in-house products/services) ads.
- Control the ads and define rules to determine where to display ads on the pages.
- Monitors and tracks the performance of ads.
Google Ad Manager Versions
There are two types of Google Ad Manager accounts – Google Ad Manager for Small Business and Google Ad Manager 360. Let’s have a quick overview of both types.
Google Ad Manager for small business
GAM for Small Business is a free version of Ad Manager, and it is designed for small to medium-sized publishers. With this version, you can have:
- 90 million monthly display ad impressions to 200 million monthly display ad impressions based on the country*, and
- Eight hundred thousand monthly video ad impressions monthly.
In addition to the ad serving, it provides various decent features, including reporting and access to API.
However, these features are limited since it is a free version designed for publishers with a few million impressions. To use advanced features and serve ad impressions more than the threshold, a publisher has to upgrade to Google Ad Manager 360.
Google Ad Manager 360
Google Ad Manager 360 is the premium or paid version of Ad Manager. It provides access to features including advanced reporting, video solutions (hosted video size limit, interactive ad formats, etc.), audience solutions for better segmentation, etc. Not only this, but you can also get direct access to Google support, integrate Google’s Data Studio for better reporting, and more.
Basic Google Ad Manager Terminologies
- Inventory: The ad units available for you to sell are called inventory. These can be grouped into various categories.
- Tags: The HTML and JavaScript codes placed on your website to link ad units to your inventory.
- Placement: The pattern of various ad units.
- Trafficking: Ad trafficking is the process of creating and managing ad campaigns. You can create inventory by targeting a specific audience.
- Ad unit: Ad Units are the places on a web page where an ad or group of ads can appear.
- Forecasting: Depending on the website impressions, Forecasting calculates the ad inventory needed in the future. It prevents the overselling of inventories.
- Reporting: The process of analysing the ad data to see the performance of every ad is called Reporting. These customizable reports enable you to create a more effective ad campaign.
How Does Google Ad Manager Work?
As Google Ad Manager is an ad server, publishers use it to manage their direct and indirect advertisers. At a basic level, the Ad Manager works as described below:
- A publisher defines the ad inventories (or ad units) in the ad server. There are a variety of ad unit sizes available in Google Ad Manager.
- While defining, they can generate the ad tags to add to the page’s source code. These ad tags are snippets of HTML or JavaScript code.
- Publisher creates line items* and orders that are ad campaigns and represent the type of advertisers.
- When the user visits a web page, the ad tag requests to return an ad from GAM.
- The ad Manager finds the right advertisers (or, you can say line items) according to the details sent via the ad request and displays the ad on the specified inventory.
*Line item is the primary element in Google DFP that helps the ad server decide which ad to serve, how, and when. Here’s a complete guide that you can refer to understand everything about line items.
Google Ad Manager: When Do You Need It?
Getting more than 500,000 monthly visitors on your website? It’s high time to sign up for Google Ad Manager. Google Ad Manager would be needed if:
- You want to manage both direct and programmatic advertising campaigns in one place,
- You want to take advantage of Google’s marketplace Ad Exchange and
- You want to run multiple ad networks/SSPs/exchanges to increase the demand for your ad inventories.
*SSPs and Ad exchanges are the intermediaries that connect you to the advertisers. Unlike Google AdSense or any other ad network, SSPs and Ad Exchanges can offer you to sell your ad inventories to multiple advertisers in real time and at higher eCPM rates.
Is Google Ad Manager an Ad Server or an SSP?
Both. As Google says, “Not just an ad server or sell-side platform (SSP),” Google Ad Manager is a complete platform that can act as an ad server and an SSP. How does it behave like an SSP? Since Google integrated its Ad Exchange into Ad Manager, Google Ad Manager enables publishers to bring additional demand via AdX.
 Google Ad Manager vs. Google AdSense
Google Ad Manager vs. Google AdSense
Although Google AdSense and Ad Manager enable publishers to sell ads on their websites, each offers different features and services. AdSense is an ad network that helps publishers sell their bulk of ad inventories to Google Ads advertisers.
GAM allows you to sell your ad inventories to Google and non-Google advertisers. Because Adsense is an ad network, you cannot connect with other ad networks to monetize your ad inventories. However, with Google Ad Manager, you can.
Moreover, there are various other differences between Google Ad Manager and Google AdSense that we have outlined here.
Can you use AdSense with Google Ad Manager?
Of course. It is recommended that publishers use Google AdSense and Ad Manager to maximize ad revenue. How does it increase revenue?
Selling all of the ad inventories is essential to reach the potential revenue. However, many publishers cannot sell all ad inventories every time. In such situations, Google AdSense helps to sell unsold ad inventories to its Google advertisers. Serving a Google ad is better than leaving the inventory remnant, right?
You can run multiple other ad networks along with Google AdSense to increase the yield further. But make sure that other ad networks are compatible with AdSense. Here is a detailed guide on how to run multiple ad networks in Google Ad Manager.

Image Source: Tech Crunch
Google Ad Manager vs. Google Ads
Google Ad Manager and Google Adsense are platforms that help publishers put ads in their inventory space. In contrast, Google Ads is a platform that helps advertisers find an inventory space in Google SERP and Google’s Ad Network.
To be exact, Google Ads is an advertising platform that helps advertisers to run their campaigns. But it is not DSP for advertisers like how GAM is both ad server and SSP for publishers. Google’s DSP for advertisers is Google DV360 (Display and Video 360). It also acts as a third-party ad server for advertisers.
So there is a clear distinction between GAM and Google Ads, which is GAM is publisher-focused, and Google Ads is for the demand side, i.e., for advertisers. They each serve as a one-stop solution for publishers and advertisers for website monetization and ad campaigns.
Google Ad Manager Account: How to Set It Up?
Signing up for GAM isn’t rocket science. But there is a prerequisite to joining Google Ad Manager, i.e., having an active AdSense account. If you have an AdSense account, you’re just a few steps away from accessing Ad Manager. Go to the Ad Manager’s home page and fill in the details as required.
After filling in the details, you need to wait a few days to get approval from Google. Once you get the approval, you can set up the ads in Google Ad Manager. Don’t know how to do it? We are here to help you. Follow the steps to set up Google DFP.
How do you Link Google AdSense to Google Ad Manager?
So, you have set up the ad units and are ready to start serving ads via Google Ad Manager. Now, why not link AdSense to Ad Manager so that you can fill the remnant ad inventories? Sounds great? Let’s have a glimpse of the required steps:
- Sign in to your Google Ad Manager.
- Navigate to Admin > Linked accounts.
- Go to the AdSense tab and click the New AdSense link.
- Enter the property code (publisher ID) associated with your AdSense account. A property code looks like this: ca-pub-1234567890.
- Enter the name and the same name will be selected when creating the AdSense line item.
- Enter the other details, such as email address, contact details, etc, and save the information.
Also, you need to enable the linking of AdSense in the AdSense account.
- Go to the AdSense account. Go to Account > Access and authorization > Third-party access. Find the request for Ad Manager and click Authorize.
When you’re done with linking AdSense to the Ad Manager, you need to make a few changes in the Ad Manager to serve ads via AdSense. Here’s an article to help you with that.
Ad formats Offered in Google Ad Manager
Unlike AdSense, Google Ad Manager is not limited to image or text ads. You can serve a long list of ad formats via Google’s ad server. Such ads can run on websites, applications, and videos. Since we believe that you’re familiar with display ads, let’s have a quick introduction to other ad formats available in Google Ad Manager:
Native ads: Native ads are the ads that match the look and feel of the organic content of the website. Such ad formats can appear in different names, such as recommended widgets, sponsored ads, promoted ads, etc. Check out this step-by-step guide to learn more about serving native ads through Google Ad Manager.
Like native ads, you can serve Multiplex ads via Google Ad Manager.
Responsive ads: Today, our audiences are everywhere—desktop, mobile, tablet, etc. Google Ad Manager helps publishers deliver responsive ads so publishers do not compromise with the user experience. Responsive ads are the ad types that can adjust their size and fit into the devices they will serve. Learn more about how to set up responsive ads in Ad Manager in this article.
Video ads: For those who have been in digital advertising for a while, you might already know what video ads are. The video ad format consists of a video in the ad and can be played with or without video content. In Google Ad Manager, you can add any video ad unit, i.e., instream and out-stream. Here’s a guide to help you how to get started with video ads in Google Ad Manager.
Google Ad Manager Price
Publishers can use GAM for free, which is one of the vital reasons for GAM’s popularity. They offer free service to up to 90 million monthly display ad impressions for North America, Australia, and New Zealand publishers.
The amount is higher in other regions, such as 150 million to 200 million impressions. Eight hundred thousand monthly video impressions are offered free in GAM’s small business plan.
The minimum eligibility the publishers need to have to access GAM is an approved AdSense account. If the publisher has passed the free limit of impressions, they must use GAM 360. The GAM 360 price varies based on impressions, with an annual fee of around $100,000 to $150,000.
Google Ad Manager Benefits
Google Ad Manager has been hailed as one of the best ad servers for its numerous benefits for publishers. Here are some of the key advantages of GAM that you should know:
Simple user interface
One of the most important aspects of ad-tech products is the user interface. Having a beginner’s mind, Google has designed the user interface of Ad Manager as simple as possible in terms of navigation and task orientation.
It makes sure to show the right amount of information on a single screen in an organized way. You can find all the necessary elements of an ad campaign on the left sidebar of the Google Ad Manager Home page. Additionally, if you don’t understand a particular UI element, you can simply click “?” and the Ad Manager will display the explanation and additional information.
Targeting capabilities:
A relevant audience is extremely important to scale up the ad revenue for the publishers. By using Google Ad Manager, you can display targeted ads based on common factors such as:
- User domain,
- Mobile carrier,
- Bandwidth (Cable, Commercial broadband, etc.),
- Device manufacturers (Amazon, Ericsson, etc.),
- Device capability (Phone calls, Mobile apps, etc.),
- Browser language,
- Operating system,
- Browser (Firefox 1.0, Firefox 1.5, etc.),
- Device category (Desktop, tablet, smartphone, etc.).
In addition to the factors above, you can target the audience based on custom parameters via key-value targeting.
Reporting Features:
Google Ad Manager offers various insights into how the ad campaigns are performing. If a user views/clicks an ad with the ad server, you can track that. By looking at which ads get clicks and which don’t, you’ll quickly see where to invest your time.
Formerly known as “Queries,” the ad server provides different reports, including pre-defined templates, so that new publishers can create reports on common data. Using Google Ad Manager reports*, you can find valuable information and data about how much a particular advertiser pays you, how many impressions ads get, and more*.
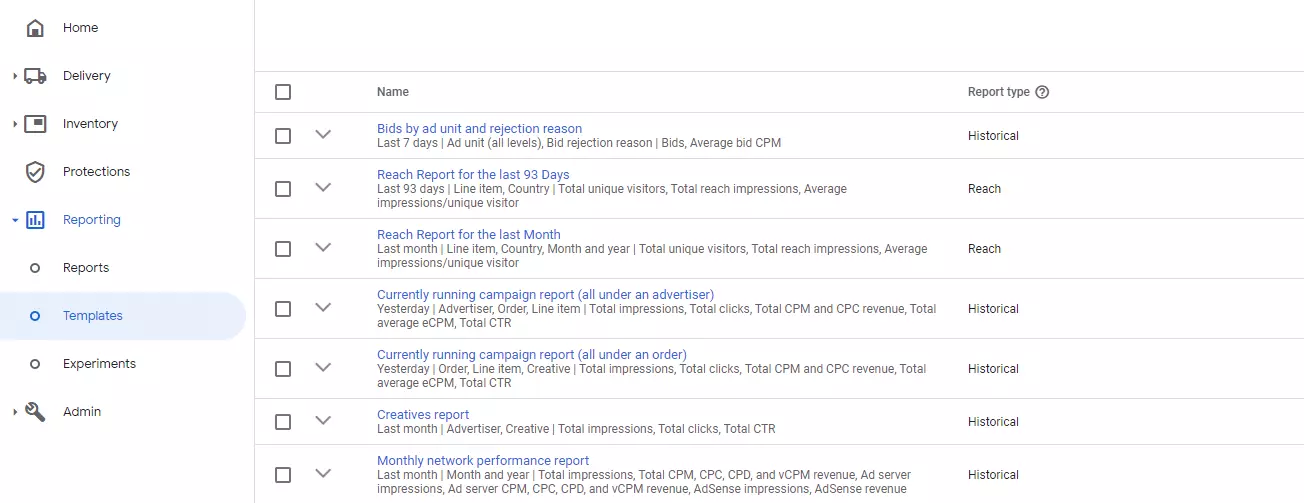
*By using key values and reporting features together, you can gain insights into various custom parameters such as how an on a particular page performed, how an ad size 720×90 performed, and so on.
Testing environment:
The importance of ad testing is imperative. A lot of times, publishers skip this process. Therefore, the ad experience and user experience might be affected. To understand how the ads will look on the website, Google Ad Manager provides a testing environment for publishers.
With this testing feature of the ad server, you can create dummy advertisers and ads and notice how user experience is being affected. You can do A/B testing with different ad units and see which layout looks better. This is just an example to illustrate the types of testing in the Ad Manager. Read this article to learn how to test your ads on the ad server.
Organizing your Ad Partners in Google Ad Manager
If you already have an ad partner, organizing them in Google Ad Manager is quite simple. Some best practices to Organize your Ad partners are as follows:
- Each advertiser should be created under a separate order number. This will simplify your reporting.
- Maintain a considerate hierarchy of orders and campaigns.
- Always use passbacks so that your unfilled inventories get filled by the house line items or any other passback network by GAM. Thus, there is no impression left unattended. (Hint: You can also use ‘Header Bidding‘, which increases your revenue and eliminates the need for passbacks).
Final Thoughts
Google Ad Manager is the leading platform in the advertising industry. As a unified solution, it has the advantage of easier setup, maintenance, and administration. Some publishers may find it overwhelming initially, but investment in Google Ad Manager is worth it.























