Programmatic advertising has transformed digital advertising, enabling advertisers to buy ad impressions in real-time through Real-Time Bidding (RTB). Apart from header bidding, programmatic direct, and private marketplaces, this efficient and automated approach has led to the rise of Open Bidding. In open bidding, publishers can offer their ad inventory to multiple demand sources in a single auction.
If you’re new to the term or want to learn more about it, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a deep dive into Google Open Bidding, how it works, and what benefits it offers to publishers. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving world of programmatic advertising.
Table of Contents
- What Is Open Bidding?
- How Does Open Bidding Work?
- Benefits of Open Bidding for Publishers
- How to Setup Open Bidding?
- Is Open Bidding Compatible With the Multiple Customer Management Program?
- Limitations of Open Bidding for Publishers
- Open Bidding Vs. Header Bidding: Which One Is Better?
- Can You Run Open Bidding With Header Bidding?
- Maximize Your Revenue With Automatad
What Is Open Bidding?
Open Bidding is Google’s server-side header bidding solution that allows multiple demand partners (e.g., Google’s Authorized Buyers and third-party ad exchanges, SSPs, and ad networks) to compete in a unified auction. Google introduced it in 2018.
With Open Bidding, publishers can simplify their ad serving by managing all demand sources from a single platform, allowing for greater transparency and control. This programmatic solution offers several benefits to publishers, including increased competition and demand for ad inventory, improved yield management, and the ability to connect with multiple demand sources through a single integration.
Unlike traditional waterfall that prioritizes the demand partners based on historical averages and calls them one at a time, Open Bidding enables you to run a unified auction that forces all demand partners (including Google) to compete simultaneously.
By running auctions in parallel, Open Bidding ensures that the highest bidder wins every impression. This leads to a better allocation of ad dollars––more fills and higher publisher revenue––with fewer chances for low ad fill rates or eCPMs.
How Does Open Bidding Work?
Now that you know what Google’s Open Bidding is, let’s look at the Open bidding process and how the auction goes down:
- A user visits your website. The first step is to send the ad request to Google Ad Manager via Google Publisher Tags (GPT). Each ad request contains information about the user, device, and targeting.
- Ad Manager selects the best eligible line items from Guaranteed campaigns.
- The server sends bid requests to third-party demand partners and Google Authorized Buyers. The server uses ‘Yield Group’ and sends bid requests to eligible demand partners in each group to collect the highest bid from them.
- Once the Ad Manager receives bids from all yield groups, it runs a unified auction. It compares the bid from direct deals (Guaranteed campaigns, etc.), Google Authorized Buyers, and other demand partners.
- After the auction is over, a winner (who bids the highest) is selected*, and the ad creative is served to the user.
Open Bidding is a server-side solution, meaning the auction occurs on the server rather than the user’s browser. This approach ensures that all bids are evaluated equally, resulting in a fair and transparent auction.
To use Open Bidding, publishers must integrate their ad server with Google Ad Manager, which acts as a central platform for managing all demand sources. The Ad Manager then sends ad requests to all demand sources simultaneously, and the winning bid is returned to the Ad Manager, which then serves the ad to the user.
*Note: Google ensures that the Guaranteed Campaigns are delivered on time, irrespective of the Open Bidding winner.
Benefits of Open Bidding for Publishers
Open Bidding offers a range of benefits to publishers, including:
- Increased Competition: Open Bidding allows multiple demand sources to compete for ad inventory in a unified auction. This competition increases demand for the publisher’s inventory, leading to higher CPMs and increased revenue.
- Reduced latency: Direct server-to-server connections to third-party ad exchanges or SSPs in Open Bidding reduces latency for a more seamless user experience. Besides, if an ad request takes longer than 160 milliseconds, it will time out in the auction. Thus, reducing the latency to a greater extent.
- Reporting and Analytics: Improved reporting makes it easier for publishers to identify revenue-generating sales channels and prioritize them for maximum revenue yield quickly and easily. Ultimately, reporting and analytics in Ad Manager provide transparency into all sales channel relationships.
- Reduced operational complexity: Setting up Open Bidding only takes a few minutes and doesn’t involve any technical skills. Unlike in the case of Header Bidding*, where you must add the JavaScript code to your site and run the auction, Google takes care of that for you when you implement Open Bidding. Hence, it reduced operational complexity.
- Greater Control: Open Bidding allows publishers to manage and optimize ad inventory across multiple demand sources from a single platform. This provides greater control and transparency, enabling publishers to maximize revenue and manage their inventory effectively.
- Easy Implementation: Open Bidding is easy to implement, requiring minimal technical expertise and integration with Google Ad Manager, a widely used ad-serving platform. This makes it accessible to publishers of all sizes and technical abilities.
*Sidenote: With an Open-source Header Bidding solution like Prebid, you must have in-depth tech skills or outsource the ad-ops. However, a Managed Header Bidding solution can help you manage everything – from setting up ad tags to optimizing the ad campaigns.
How to Setup Open Bidding?
To set up Open Bidding, you will need to follow these steps:
- Check Eligibility: First, you must check whether you can use Open Bidding. Open Bidding is available only for publishers using Google Ad Manager and approved to use Google Ad Exchange.
- Choose Demand Partners: You must select the demand partners you want to participate in your Open Bidding auction. Google Ad Exchange and other third-party exchanges can be used.
- Configure the Ad Units: You must configure your ad units to work with Open Bidding. This involves setting the floor price for your ad inventory and configuring the ad unit settings for Open Bidding.
- Set-Up Line Items: You must set up line items for each demand partner you want to include in your Open Bidding auction. This involves creating a line item in Google Ad Manager and configuring it to work with Open Bidding.
- Implement the Code: Once you have set up your line items, you must implement the Open Bidding code on your website. This code will enable your ad units to participate in the Open Bidding auction and receive bids from multiple demand partners.
- Monitor Performance: After you have set up Open Bidding, you will need to monitor its performance and make adjustments as needed. This involves analyzing the performance data from Google Ad Manager and optimizing your Open Bidding settings to achieve the best results.
We have discussed in detail the steps required to enable Open Bidding and check the performance in your Ad Manager account. Don’t forget to explore.
Is Open Bidding Compatible With the Multiple Customer Management Program?
MCM is a flexible and robust program that allows publishers to manage relationships with multiple clients or brands within a single Ad Manager account.
By using MCM, publishers can easily set up Open Bidding as well as Programmatic Guaranteed or Direct deals. This can help simplify the management of your ad inventory and streamline your operations, allowing you to focus on maximizing your revenue.
Attention Please: We have been handpicked by Google to be a partner for its MCM program. So, if you are excited to reap the benefits of Google’s MCM program, we are just a click away.
Limitations of Open Bidding for Publishers
While Open Bidding has its benefits, there are also some limitations that publishers should be aware of before implementing it on their websites. Here are a few:
Low Match Rates: Open Bidding is disadvantaged by the fact that the ad request is sent by the ad server, not by the user’s browser. This affects the match rates as DSPs cannot synchronize cookies and identify the users*. It could result in some very low-performing and irrelevant ads showing up on your site, leading to a decline in revenue.
“Supply-side platforms running server-side would no longer have access to the user’s browser and, much as demand-side platforms are doing now, will have to sync with the one player that has the tag down and is initiating the call from the browser. The concern is that this may lead to reduced match rates and lower yields on unmatched users.”
– Digiday
*This could change based on the adoption of identity solutions once third-party cookies get completely disabled by Google.
Technical Complexity: Setting up and managing Open Bidding can be technically challenging for some publishers, especially those with limited technical resources or expertise.
Less Transparency: Google manages every aspect of ad serving, including billing, reporting, inventory, and optimization. You will have no control over which ad wins in the auction, and the server will decide to deliver the winning ad. Thus, reducing transparency.
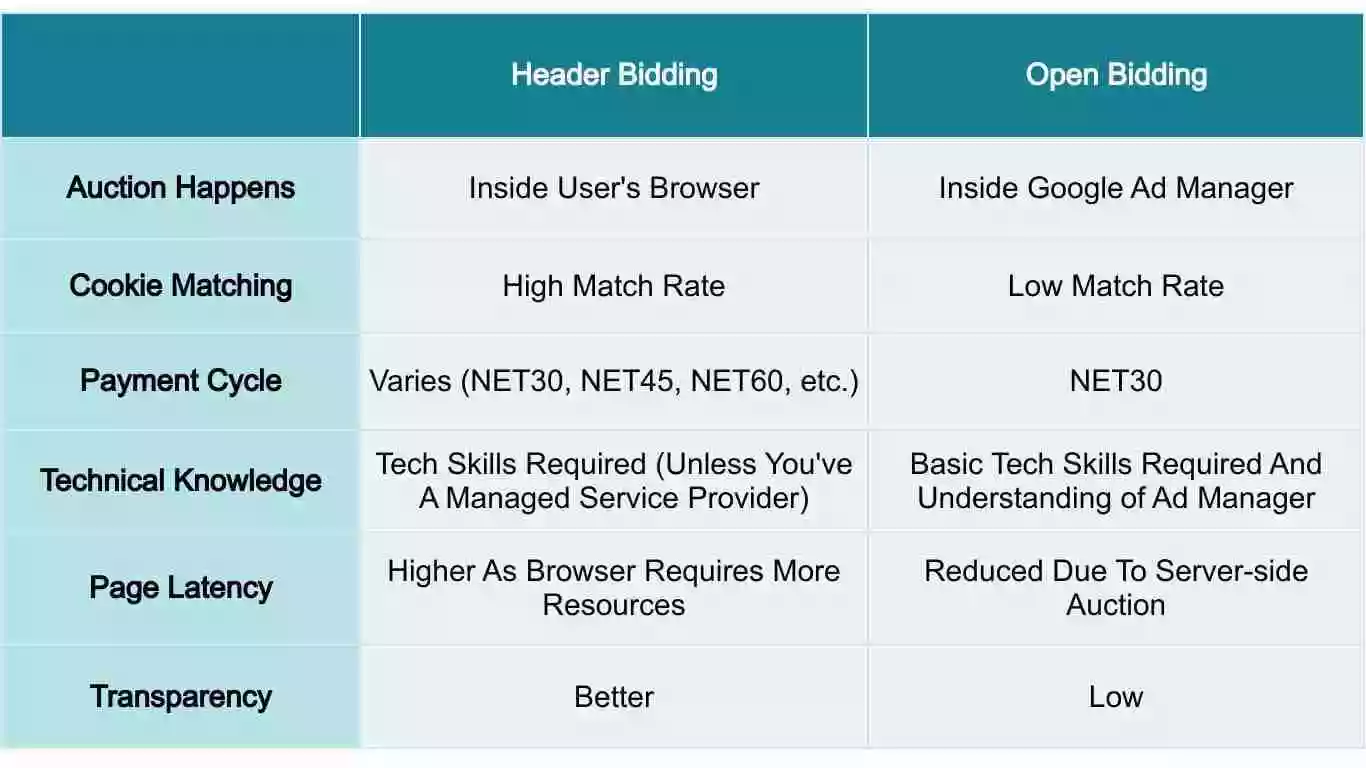
Open Bidding Vs. Header Bidding: Which One Is Better?
We already know that a bold statement like ‘the best way to get more revenue is by investing in different techniques’ cannot be simply true for all.
Open Bidding is right if you focus on improving user experience and emphasizing less about eCPM. You might be able to reduce the latency, but that may sacrifice the revenue. In contrast, Header Bidding is a perfect solution if your primary goal is to increase eCPM. You might be able to get higher revenue, but you need to put extra effort into dealing with the latency issues that arise*.
*Please note that an ideal or right header bidding solution will have little to no impact on page loading speed and doesn’t affect user experience.
Check out this article for a detailed comparison of both RTB techniques. Or have a brief overview here:
Can You Run Open Bidding With Header Bidding?
Yes, it is possible to run Open Bidding alongside Header Bidding. In fact, many publishers use both techniques to optimize their ad revenue. However, it is important to ensure that there is no conflict between the two techniques, as it could result in issues such as latency, decreased page speed, and higher bounce rates.
One way to avoid conflicts is to use a wrapper that can manage both Open Bidding and Header Bidding. The wrapper would send out a single ad call allowing both techniques to bid and compete for the impression. This can improve the chances of getting higher bids and better fill rates. Automatad header bidding wrapper does just that. We run a unified auction, ensuring you get the best out of your ad inventory.
Maximize Your Revenue With Automatad
As the world of programmatic advertising continues to evolve, publishers must stay on top of the latest trends and technologies to maximize their revenue potential. Open Bidding has proven to be a valuable tool for publishers looking to tap into larger ad budgets and increase their bottom line, but it’s not the only option out there.
At Automatad, we understand that every publisher has unique needs and goals, so we offer customized solutions tailored to your business. Whether you’re interested in Open Bidding, header bidding, or a combination of both, our team of experts can help you navigate the complex landscape of programmatic advertising and find the best solution for you.
By partnering with Automatad, you’ll gain access to cutting-edge technology that streamlines your monetization process, giving you more time to focus on creating high-quality content for your audience. Plus, our commitment to transparency and data-driven insights means you’ll always have a clear picture of your ads’ performance and where your revenue comes from.
Don’t wait any longer to unlock your full revenue potential. Sign up with Automatad today and start seeing the results you’ve been dreaming of!
FAQs
Q1. How does Google open bidding work?
Google Open Bidding is a programmatic advertising feature that allows publishers to invite demand sources to compete in real-time to display ads on their websites.
Q2. How do I enable open bidding?
You must have a Google Ad Manager account, create an Open Bidding addendum, and establish partnership agreements with each demand partner to enable Open Bidding. Once done, you can set up line items, ad units, demand partners, etc.
Q3. What is the difference between Closed and Open Bidding?
Closed Bidding is an auction in which a small group of advertisers are invited to bid on ad inventory. In contrast, Open Bidding allows all eligible advertisers to bid on inventory in real-time.























